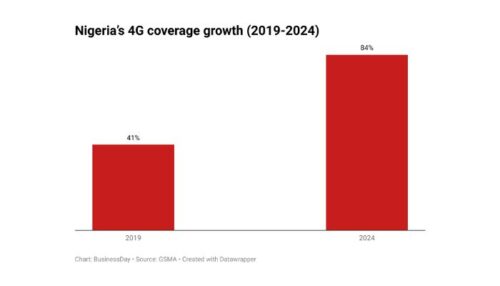
Nigeria’s 4G network coverage has significantly expanded, reaching 84% in 2024, a substantial rise from just 41% in 2019, according to a recent GSMA report.
The report, titled “Sub-Saharan Africa 2024 Year in Review,” highlights the remarkable progress made in expanding 4G access across the country. However, it points out ongoing challenges, particularly in rural regions, where coverage still lags at 48%.
GSMA’s analysis underscores the urgent need for further investment to bring 4G connectivity closer to nationwide coverage. Estimates suggest that achieving 98% coverage would require an additional $360 million in funding. The remaining 2% of the population, residing in hard-to-reach rural areas, may have to rely on alternative technologies like satellite internet to stay connected.
Read also: How MTN’s NTEL spectrum lease will enhance mobile broadband expansion
The report also suggests that targeted policy reforms could play a crucial role in bridging the funding gap. By removing sector-specific taxes on telecom infrastructure and relaxing retail pricing controls, the financial requirement could be reduced by 44%, lowering the necessary investment to around $200 million.
Additionally, GSMA emphasizes the need for policies that promote affordability and accessibility of 4G-enabled devices. If adoption rates increase and revenue per user matches those in other African markets, Nigeria could achieve 97% coverage, potentially slashing the investment requirement to a mere $30 million.
The growth in 4G coverage—from 41% to 84% within five years—demonstrates the efforts of telecom providers and government agencies in enhancing digital connectivity. However, the gap between urban and rural access remains a challenge, as deploying infrastructure in low-income areas continues to be economically demanding.
Expanding 4G availability is crucial for Nigeria’s economic development, offering better internet access, driving digital innovation, and fostering socio-economic progress across various sectors.


