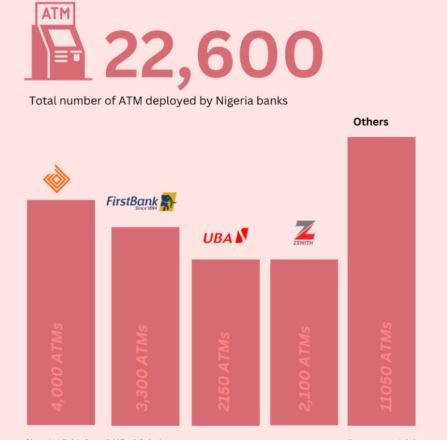
Nigeria’s growing population and expanding financial services sector have led to an increased demand for ATMs. However, the country’s ATM infrastructure is facing significant challenges, including rising costs, regulatory hurdles, and changing consumer preferences.
Several factors contribute to the challenges faced by the ATM industry in Nigeria:
- High Operating Costs: The rising costs of maintenance, security, and electricity, coupled with the devaluation of the Naira, have made it increasingly expensive to operate ATMs.
- Regulatory Constraints: Strict regulations imposed by the Central Bank of Nigeria, such as fixed transaction fees, limit the profitability of ATM operations.
- Shifting Consumer Preferences: The increasing popularity of digital banking and mobile payments has reduced the reliance on traditional ATMs.
- Infrastructure Challenges: Poor power supply and network connectivity can disrupt ATM services, leading to customer dissatisfaction.
To address these issues, stakeholders in the Nigerian financial industry need to collaborate to find innovative solutions. This may involve exploring alternative payment methods, optimizing ATM networks, and leveraging technology to improve efficiency.
Furthermore, the government can play a crucial role by providing supportive policies and incentives to promote the development of a robust and sustainable ATM infrastructure. By working together, the industry can ensure that ATMs remain a vital component of Nigeria’s financial landscape.